Pointer is a user defined data type which creates special types of variables which can hold the address of primitive data type like char, int, float, double or user defined data type like function, pointer etc. or derived data type like array, structure, union, enum.
Examples:
int *ptr;
int (*ptr)();
int (*ptr)[2];
In c programming every variable keeps two type of value.
1. Contain of variable or value of variable.
2. Address of variable where it has stored in the memory.
(1) Meaning of following simple pointer declaration and definition:
int a=5;
int * ptr;
ptr=&a;
Explanation:
About variable a:
1. Name of variable : a
2. Value of variable which it keeps: 5
3. Address where it has stored in memory : 1025 (assume)
About variable ptr:
4. Name of variable : ptr
5. Value of variable which it keeps: 1025
6. Address where it has stored in memory : 5000 (assume)
Pictorial representation:

Note: A variable where it will be stored in memory is decided by operating system. We cannot guess at which location a particular variable will be stored in memory.
(2) Meaning of following pointer declaration and definition:
int a=50;
int *ptr1;
int **ptr2;
ptr1=&a;
ptr2=&pt1;
Explanation:
About variable a:
1. Name of variable : a
2. Value of variable which it keeps: 50
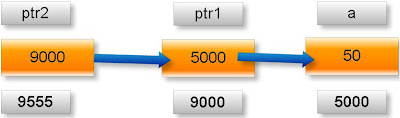
3. Address where it has stored in memory : 5000 (assume)
About variable ptr1:
4. Name of variable : ptr1
5. Value of variable which it keeps: 5000
6. Address where it has stored in memory : 9000 (assume)
About variable ptr2:
7. Name of variable : ptr2
8. Value of variable which it keeps: 9000
9. Address where it has stored in memory : 9555 (assume)
Pictorial representation of above pointer declaration and definition:
Note:
* is know as indirection operator which gives content of any variable.
& is know as reference operator which gives address where variable has stored in memory.
Cancellation rule of above two operators:
* and & operators always cancel to each other. i.e.
*&p=p
But it is not right to write:
&*p=p
Simple example:
What will be output of following c program?
void main(){
int x=25;
int *ptr=&x; //statement one
int **temp=&ptr; //statement two
printf(“%d %d %d”.x.*ptr,**temp);
}
Output: 25 25 25
Explanation:
As we know value of variable x is 25.
*ptr= *(&x) //from statement one
=*&x
=x //using cancellation rule
=25
**temp= **(&ptr)=*(*&ptr)=*ptr=*(&x)=*&x=x=25

No comments:
Post a Comment